CBSE Notes Class 12 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
CBSE Notes Class 12 Maths Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Inverse Function
If y = f(x) and x = g(y) are two functions such that f (g(y)) = y and g (f(y)) = x, then f and y are said to be inverse of each other
i.e., g = f-1
IF y = f(x), then x = f-1(y)
Inverse Trigonometric Functions
If y = sin X-1, then x = sin-1 y, similarly for other trigonometric functions.
This is called inverse trigonometric function .
Now, y = sin-1(x), y ∈ [π / 2 , π / 2] and x ∈ [-1,1].
(i) Thus, sin-1x has infinitely many values for given x ∈ [-1, 1].
(ii) There is only one value among these values which lies in the interval [π / 2 , π / 2]. This value is called the principal value.
Domain and Range of Inverse Trigonometric FunctionsGraphs of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
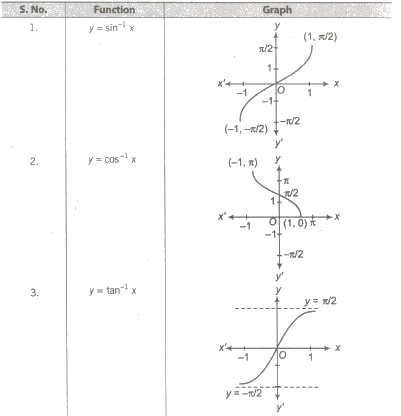
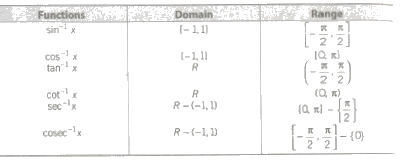
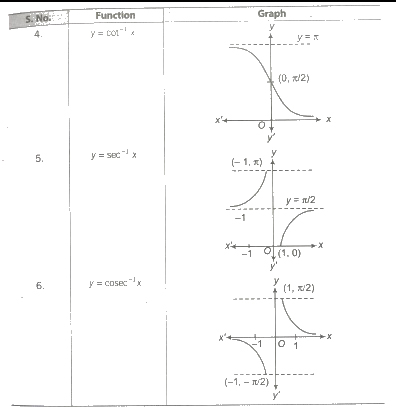
Properties of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Property I
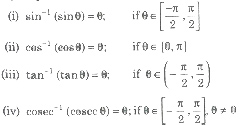
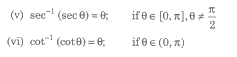
Property II
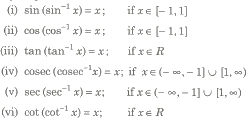
Property III
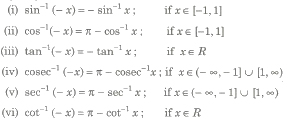
Property IV
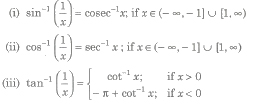
Property V
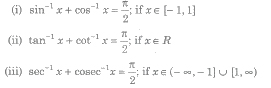
Property VI
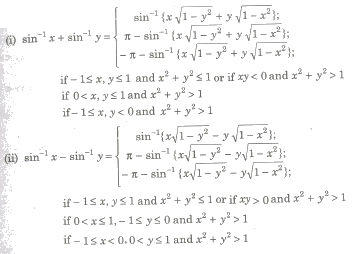
Property VII
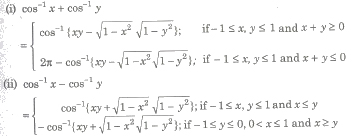
Property VIII
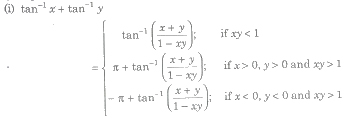
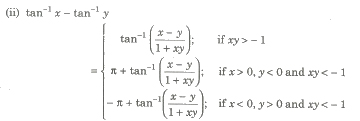
Property IX
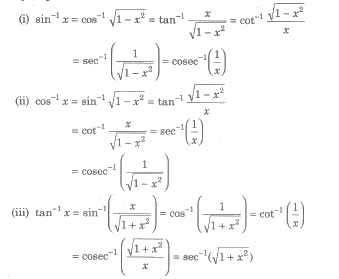
Property X
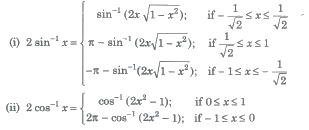
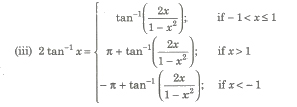
Property XI
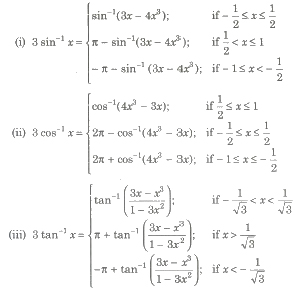
Property XII
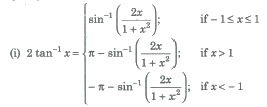
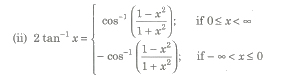
Important Results
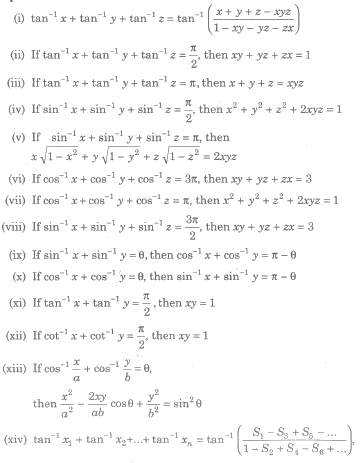
where Sk denotes the sum of the product of x1,x2,…xn takes k at a time.
Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
If sinh y = x, then y is called the inverse hyperbolic sine of x and it is written as y = sinh-1 x.
Similarly, cosh-1 x, tan h-1 x etc., can be defined,
Domain and Range of Inverse Hyperbolic Functions

Relation between Inverse Circular Functions and Inverse Hyperbolic Functions
(i) sinh-1x = – i sin-1(ix)
(ii) cosh-1x = – i cos-1 x .
(iii) tanh--1x = – i tan-1(ix)
Important Results
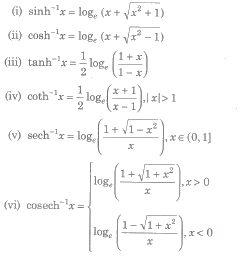
Trigonometric Equation
An equation involving one or more trigonometrical ratios of unknown angle is called a trigonometric equation .
Solution/Roots of a Trigonometric Equation
A value of the unknown angle which satisfies the given equation, is called a solution or root of the equation.
The trigonometric equation may have infinite number of solutions.
(i) Principal Solution – The least value of unknown angle which satisfies the given equation, is called a principal solution of trigonometric equation.(ii) General Solution – We know that, trigonometric function are periodic and solution of trigonometric equations can be generalised with the help of the periodicity of the trigonometric functions. The solution consisting of all possible solutions of a trigonometric equation is called its general solution.
Important Results
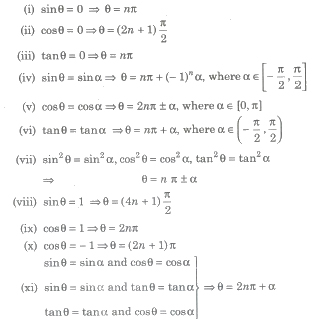
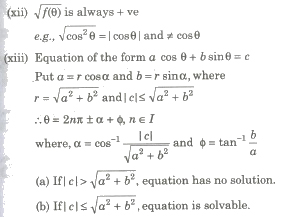
Important Points to be Remembered
(i) While solving an equation, we have to square it, sometimes the resulting roots does not satisfy the original equation.
(ii) Do not cancel common factors involving the unknown angle on LHS and RHS.Because it may be the solution of given equation.
(iii) (a) Equation involving sec θ or tan θ can never be a solution of the form (2n + 1) π / 2.
(b) Equation involving coseca or cote can never be a solution of the form θ = nπ.
For Class 11
For Class 11
